Basic Setup
HTML imports
Bun supports importing HTML files directly into your server code, enabling full-stack applications with both server-side and client-side code. HTML imports work in two modes: Development (bun --hot): Assets are bundled on-demand at runtime, enabling hot module replacement (HMR) for a fast, iterative development experience. When you change your frontend code, the browser automatically updates without a full page reload.
Production (bun build): When building with bun build --target=bun, the import index from "./index.html" statement resolves to a pre-built manifest object containing all bundled client assets. Bun.serve consumes this manifest to serve optimized assets with zero runtime bundling overhead. This is ideal for deploying to production.
Configuration
Changing the port and hostname
To configure which port and hostname the server will listen on, set port and hostname in the options object.
port to 0.
port property on the server object, or by accessing the url property.
Configuring a default port
Bun supports several options and environment variables to configure the default port. The default port is used when theport option is not set.
--portCLI flag
BUN_PORTenvironment variable
PORTenvironment variable
terminal
NODE_PORTenvironment variable
terminal
Unix domain sockets
To listen on a unix domain socket, pass theunix option with the path to the socket.
Abstract namespace sockets
Bun supports Linux abstract namespace sockets. To use an abstract namespace socket, prefix theunix path with a null byte.
idleTimeout
By default,Bun.serve closes connections after 10 seconds of inactivity. A connection is considered idle when there is no data being sent or received — this includes in-flight requests where your handler is still running but hasn’t written any bytes to the response yet. Browsers and fetch() clients will see this as a connection reset.
To configure this, set the idleTimeout field (in seconds). The maximum value is 255, and 0 disables the timeout entirely.
Streaming & Server-Sent Events — The idle timer applies while a response is being streamed. If your stream goes
quiet for longer than
idleTimeout, the connection will be closed mid-response. For long-lived streams, disable the
timeout for that request with server.timeout(req, 0).export default syntax
Thus far, the examples on this page have used the explicitBun.serve API. Bun also supports an alternate syntax.
server.ts
<undefined> represents WebSocket data — if you add a websocket handler with custom data attached via server.upgrade(req, { data: ... }), replace undefined with your data type.
Instead of passing the server options into Bun.serve, export default it. This file can be executed as-is; when Bun sees a file with a default export containing a fetch handler, it passes it into Bun.serve under the hood.
Hot Route Reloading
Update routes without server restarts usingserver.reload():
Server Lifecycle Methods
server.stop()
To stop the server from accepting new connections:
stop() allows in-flight requests and WebSocket connections to complete. Pass true to immediately terminate all connections.
server.ref() and server.unref()
Control whether the server keeps the Bun process alive:
server.reload()
Update the server’s handlers without restarting:
fetch, error, and routes can be updated.
Per-Request Controls
server.timeout(Request, seconds)
Override the idle timeout for an individual request. Pass 0 to disable the timeout entirely for that request.
idleTimeout for every request:
server.requestIP(Request)
Get client IP and port information:
null for closed requests or Unix domain sockets.
Server Metrics
server.pendingRequests and server.pendingWebSockets
Monitor server activity with built-in counters:
server.subscriberCount(topic)
Get count of subscribers for a WebSocket topic:
Benchmarks
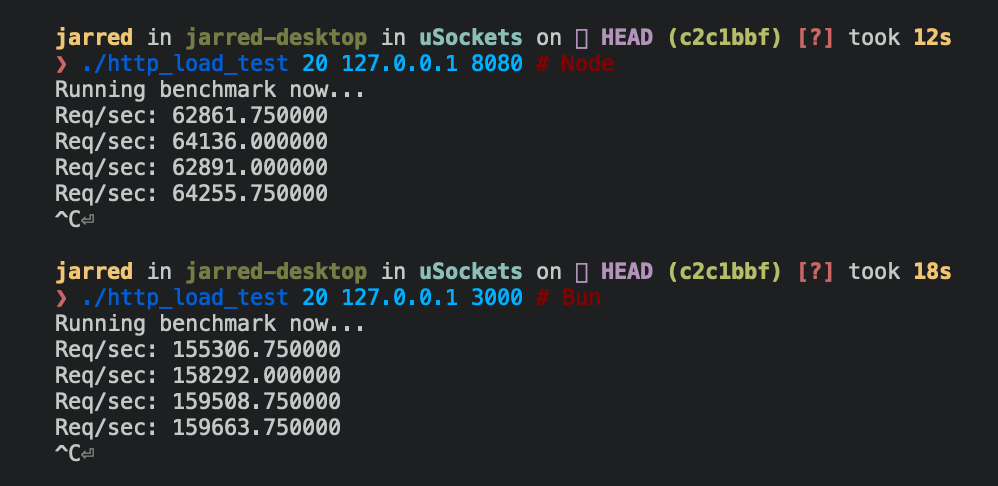
Below are Bun and Node.js implementations of a simple HTTP server that respondsBun! to each incoming Request.
Bun
Bun.serve server can handle roughly 2.5x more requests per second than Node.js on Linux.
| Runtime | Requests per second |
|---|---|
| Node 16 | ~64,000 |
| Bun | ~160,000 |
Practical example: REST API
Here’s a basic database-backed REST API using Bun’s router with zero dependencies:Reference
See TypeScript Definitions